Choosing the right heat pump is crucial for ensuring optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term savings. Here are steps and factors to consider when selecting a heat pump:
- Determine the Type of Heat Pump Needed:
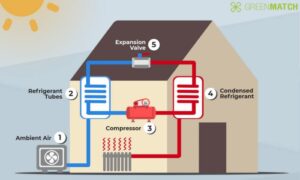
- Air-Source Heat Pump (ASHP): Extracts heat from outdoor air. Suitable for most climates, but its efficiency can decrease in extremely cold temperatures.
- Ground-Source or Geothermal Heat Pump: Extracts heat from the ground or groundwater. More expensive to install but offers higher efficiency, especially in colder climates.
- Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pump: Suitable for homes without existing ductwork or for targeted heating/cooling of specific rooms.
- Absorption Heat Pump: Powered by natural gas, propane, or solar-heated water, suitable for larger homes or commercial properties.
- Assess Your Climate:
- If you live in a colder region, consider a heat pump designed for cold climates (Cold Climate Air-Source Heat Pump, ccASHP). Look for models with a high Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF).
- Size it Right:
- A heat pump that’s too large will cycle on and off too frequently, reducing its efficiency and lifespan. One that’s too small won’t adequately heat or cool your home.
- Consult with a HVAC professional to conduct a detailed load calculation for your home. This considers factors like the size of your home, insulation levels, window types, and local climate to determine the best size.
- Check Efficiency Ratings:
- HSPF: For heating efficiency. Higher values are better.
- Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER): For cooling efficiency. Higher values are better.
- Coefficient of Performance (COP): Another measure of efficiency. Higher values are better.
- Energy Star Label: Heat pumps that meet specific efficiency criteria will have this label.
- Consider Advanced Features:
- Variable Speed or Dual-Speed Compressors: Adjust to the heating or cooling needs, improving comfort and efficiency.
- Desuperheaters: Reclaim excess heat from the heat pump’s cooling mode to heat water at a low cost.
- Backup Burners: Helps supplement heating during extremely cold periods.
- Review Warranty and Reliability:
- Choose brands and models known for durability and reliability. Check consumer reviews and ratings.
- Understand warranty terms. Longer warranties often indicate a more reliable product.
- Evaluate Total Costs:
- Consider both the initial purchase and installation costs as well as long-term operating costs.
- While a more efficient heat pump might cost more upfront, it can lead to significant energy savings in the long run.
- Check for Incentives and Rebates:
- Many governments and utility companies offer rebates or incentives for installing energy-efficient heat pumps. This can significantly offset the initial investment.
- Consult with Professionals:
- Engage a reputable HVAC contractor with experience in heat pump installations. They can provide invaluable advice on the best options for your specific needs.
- Additional Considerations:
- Noise Level: Some units operate more quietly than others. Check the decibel rating if noise is a concern.
- Compatibility: Ensure the heat pump is compatible with existing systems (like ductwork) if you aren’t doing a full replacement.
In summary, investing time in research and consultation with professionals will ensure that you choose the right heat pump for your needs, providing years of comfort and energy savings.